Overlook sperm meets egg.
Utilizing human stem cells, scientists have created human embryo-like buildings inside petri dishes. These lab-grown blobs develop a number of buildings that mimic a human embryo after implantation into the uterus—a serious milestone for fertility—and final not less than 14 days.
A decade in the past, manufacturing embryo-like buildings, or embryoids, with out reproductive cells would have appeared ludicrous. However as scientists more and more map out the convoluted molecular journey in the direction of human conception, it’s changing into doable to cast off sperm and egg so as to peek into the “black field” of early human improvement.
It nonetheless appears like a Frankenstein experiment. However the endeavor isn’t macabre scientific curiosity. Little or no is understood in regards to the first few weeks of human being pregnant, when improvement most frequently tends to go awry. Learning fashions mimicking these early phases—with out the controversy of organic samples—may assist {couples} struggling to conceive and shine a light-weight on the mysteries of misplaced early pregnancies.
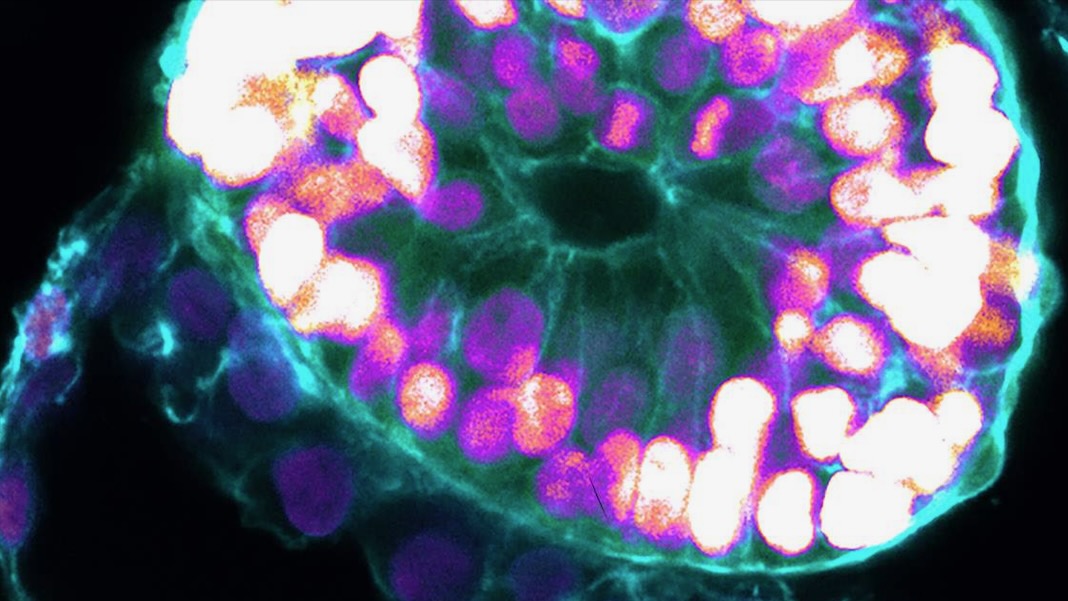
A brand new examine printed in Nature from embryoid veteran Dr. Jacob Hanna now pushes the lab-gestation timeline ahead. The workforce turned human embryonic stem cells into embryoids that mannequin early human embryos. Like their organic counterparts, the lab-based blobs developed main “layers” of tissues defining the early phases of human improvement.
“The drama is within the first month, the remaining eight months of being pregnant are primarily numerous development,” mentioned Hanna. “However that first month remains to be largely a black field. Our stem-cell-derived human embryo mannequin presents an moral and accessible manner of peering into this field.”
Recipe for an Embryoid
Two years in the past, the identical workforce launched a blockbuster consequence: egg meets sperm isn’t essential to spark life, not less than in mice. Utilizing mouse stem cells, the workforce found a chemical soup that might nudge the cells into embryo-like buildings inside a petri dish.
“The embryo is the perfect organ-making machine and the perfect 3D bioprinter—we tried to emulate what it does,” mentioned Hanna on the time.
The thought appears comparatively easy: all embryonic cells have the potential to develop into some other cell sort. However these cells are additionally extremely social. Relying on their surroundings—for instance, which chemical or hormonal indicators they obtain—they self-organize into tissues.
Culturing embryoids depends on two advances, each from the Hanna lab.
One locations reverted stem cells into a totally naïve state—a tabula rasa that wipes away any identification. We regularly consider stem cells as a uniform crowd, however they’re truly on a spectrum of improvement. Every step ahead guides the cell’s improvement in the direction of a particular cell sort or organ. Nevertheless, a naïve stem cell has the potential to develop into any physique half.
Fully rebooting to naïve stem cells makes it simpler to combine stem cells into their hosts—no matter whether or not it’s in people or mice.
One other advance is an electronically managed system that bathes the embryoids in waves of vitamins. Like a pacemaker, the pump simulates how vitamins wash over embryos within the womb, all of the whereas controlling oxygen ranges and atmospheric stress.
In a proof-of-concept examine, a small portion of cells from mice shaped into embryo-like buildings. They developed equally to their pure counterparts up till roughly half of their regular gestation. By eight days, the embryoids had a beating coronary heart, blood cells of their circulation, a mini-brain with its classical folds, and a digestive tract.
“For those who give an embryo the suitable circumstances, its genetic code will perform like a pre-set line of dominos, organized to fall one after the opposite,” mentioned Hanna in an earlier interview. “Our goal was to recreate these circumstances, and now we will watch, in actual time, as every domino hits the subsequent one in line.”
Practically Human
Mice will not be males. Hanna is effectively conscious, and the brand new examine bridges the chasm.
Step one? Prime a human stem cell by reverting it right into a naïve state.
With this uncooked materials in hand, the workforce subsequent gave the cells completely different identities, known as lineages. A few of these grow to be cells that ultimately make up the embryo. Others flip into supporting cells, resembling those who make up the placenta or construct the yolk sac—a small, rounded multitasker that helps the well being of the creating embryo.
In different phrases, the early creating human embryo is a fancy ecosystem. So, it’s no surprise that coaxing naïve stem cells into a number of roles has lengthy eluded embryoid makers. But each single lineage turns into indispensable after a serious step in early human improvement, implantation, takes place. When a fertilized embryo attaches to the uterine wall, it sparks a myriad of modifications important for additional improvement. It’s additionally when embryo loss usually happens.
The brand new examine zooms in on the post-implantation stage, repurposing the workforce’s earlier mouse embryoid protocol to generate self-organizing human embryoids. Surprisingly, it was less complicated.
They needed to genetically engineer mouse stem cells to push them in the direction of completely different lineages, the workforce says. With human cells, they only tweaked the nutrient bathtub—no further genes required—to activate genetic packages in stem cells, turning them into all three kinds of supporting tissues.
Because the embryoids matured, the workforce used a collection of molecular and genetic instruments to look at their constancy. Total, the buildings resembled the 3D structure of naturally developed human embryos between 7 to 14 days after fertilization. Some cells even pumped out human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone used for residence being pregnant assessments. Dabbing the cells’ secretions onto the stick gave the double-line constructive consequence.
Total, the embryoids confirmed key developmental landmarks of an early implanted embryo, mentioned the workforce, with out the necessity for fertilization or interactions with a mom’s womb.
Embryoid Race
Hanna’s workforce isn’t the one one pushing embryoids ahead.
In June this 12 months, two different groups engineered embryoids that mimic human embryos after implantation. The recipes and components are completely different than Hanna’s. One examine, for instance, inserted a number of highly effective genetic elements that pushed stem cells to develop into supporting tissues.
Scientists don’t fairly agree on which embryoids finest resemble their pure counterpart. Nevertheless, they do agree on one facet: stem cells, underneath the suitable circumstances, have an unbelievable skill to self-organize into more and more refined embryo-like buildings.
For now, the 14-day embryoid is touted because the “most superior” but.
Fourteen days is a strict cutoff for analysis on pure human embryos in lots of international locations, in that they’ll’t be additional cultured within the lab. Nevertheless, embryoids don’t meet the definition of an embryo and aren’t subjected to the 14-day limitation. In different phrases, human embryoids could possibly be cultured additional alongside the event timeline. Earlier work reveals it’s technologically doable in mice, with stem cells creating semi-functional organs.
For those who’re getting a bit creeped out—you’re not alone. Embryoids are rising into ever later phases in an arms race to open the black field of early human improvement. For now, embryoids grown from human embryonic stem cells should respect present rules. Nevertheless, ones created from induced stem cells—usually utilizing pores and skin cells reverted right into a stem-cell-like state—aren’t subjected to any guidelines.
To be clear, embryoids don’t have the capability to completely grow to be human beings. Nevertheless, a current examine in monkeys confirmed that they’ll induce being pregnant when transplanted right into a womb—although in that case, the embryoid was quickly and naturally terminated. Debates on if and find out how to regulate these mobile blobs are ongoing.
For now, Hanna’s workforce is targeted on a revising their recipe to spice up effectivity. However as a long-term purpose, they hope to push the embryoid even additional to see if they’ll develop rudimentary organs. These experiments “will supply insights into beforehand inaccessible home windows of early human improvement,” they are saying.
Picture Credit score: Weizmann Institute of Science