Sponsored Content material by Instaclustr, a part of Spot by NetApp

PostgreSQL®, a strong enterprise-grade open supply relational database administration system, has steadily advanced over three a long time, gaining world reputation. This weblog delves into PostgreSQL’s structure, detailing its parts and interactions. By greedy these components, you’ll be empowered to optimize database efficiency, troubleshoot points, and make knowledgeable design and scaling selections.
PostgreSQL is an open supply object-relational database administration system utilized for each transactional and analytical duties. Rooted within the SQL programming language, it boasts options for securely storing and successfully scaling advanced information workloads. With origins within the 1986 POSTGRES undertaking at UC Berkeley, it boasts over 35 years of steady improvement.
PostgreSQL’s complete options have propelled it to the forefront of database options. Addressing efficiency, safety, programming extensions, and configuration, it helps various language-based database features. Its array of knowledge varieties spans from primitives to JSONB, hstore, and arrays, and it accommodates customized advanced varieties. The system presents full-text search, strong authentication, entry management, and international information wrappers for distant information entry. Views, materialized views, JSONB doc storage, and hstore key-value pairs allow storage and retrieval of semi-structured information alongside relational information.
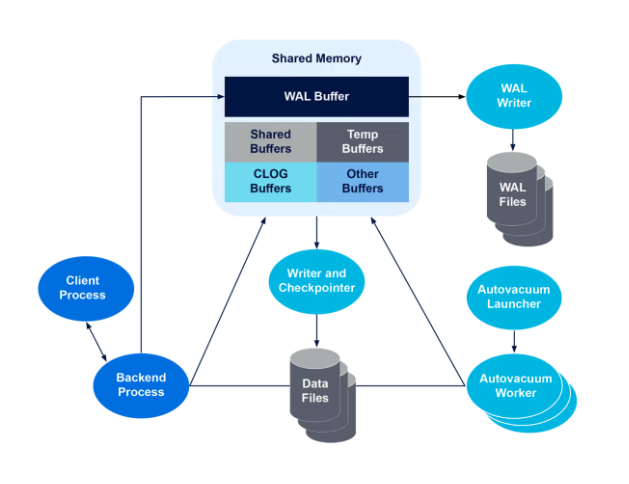
Working on the client-server mannequin, PostgreSQL accommodates a number of shoppers, whether or not native or distant. Upon consumer connection, the principle course of forks new processes for every connection, restricted by obtainable CPU cores and RAM. Connection pooling optimizes this by pre-establishing connections to serve shoppers, bettering efficiency by eliminating connection creation occasions.
PostgreSQL contains three course of classes: Server Processes, Backend Processes, and Background Employee Processes. The PostgreSQL Server Course of (previously Postmaster) manages consumer connections and backend course of initiation. Backend Processes deal with question execution and transaction administration for shoppers. Background Employee Processes carry out database upkeep and system-wide administration duties.
Reminiscence considerably influences PostgreSQL’s inter-process communication and efficiency. It’s categorized into native reminiscence, utilized by backend processes for queries, and shared reminiscence for PostgreSQL Server. Shared reminiscence facilitates inter-process communication and holds desk information. Shared Buffers and WAL Buffers improve database effectivity, caching IO operations and managing transaction logs for restoration.
Logically, PostgreSQL employs clusters, databases, schemas, tables, columns, indexes, views, features, triggers, and sequences. Clusters include databases managed by a single server, databases encompass schemas, and schemas arrange database objects. Tables maintain data in rows and attributes in columns. Indexes expedite information retrieval, views provide digital tables for question encapsulation, and constraints preserve information integrity.
Bodily, every database has its listing, with tables saved as information inside. PostgreSQL makes use of heap information for information storage. These include data of mounted lengths and are appended sequentially. Shared Buffers cache continuously accessed information, bettering efficiency.
Roles and privileges guarantee safe database entry. Roles could be assigned to people or grouped for environment friendly permission administration. Privileges dictate actions roles can carry out inside the database. PostgreSQL’s object hierarchy, together with clusters, databases, schemas, tables, columns, indexes, views, features, triggers, and sequences, facilitates organized information administration.
PostgreSQL helps bodily and logical replication, enhancing information availability and browse efficiency. Load balancing distributes queries throughout nodes, whereas excessive availability is ensured by primary-replica structure and cluster managers like Patroni.
Understanding PostgreSQL’s structure is significant for maximizing its potential. A deep grasp of its inside workings empowers you to handle challenges, optimize efficiency, and guarantee information reliability. Whereas PostgreSQL is low-maintenance, common duties like vacuuming, reindexing, and log administration are important. Instaclustr Managed Service for PostgreSQL presents skilled administration for uninterrupted software constructing and scaling.
Spin Up a Free PostgreSQL Cluster