| Jul 04, 2023 |
|
(Nanowerk Information) Rydberg states happen in a spread of bodily techniques together with atoms, molecules, and solids. Specifically, Rydberg excitons, that are extremely energetic electron-hole pairs, had been first discovered within the Cu2O semiconductor materials within the Fifties.
|
|
Latest analysis revealed in Science (“Commentary of Rydberg moiré excitons”) by Dr. XU Yang and his workforce from the Institute of Physics (IOP) of the Chinese language Academy of Sciences (CAS), and a bunch led by Dr. YUAN Shengjun from Wuhan College, stories the remark of Rydberg moiré excitons. These are moiré-confined Rydberg excitons within the WSe2 monolayer semiconductor, subsequent to small-angle twisted bilayer graphene (TBG).
|
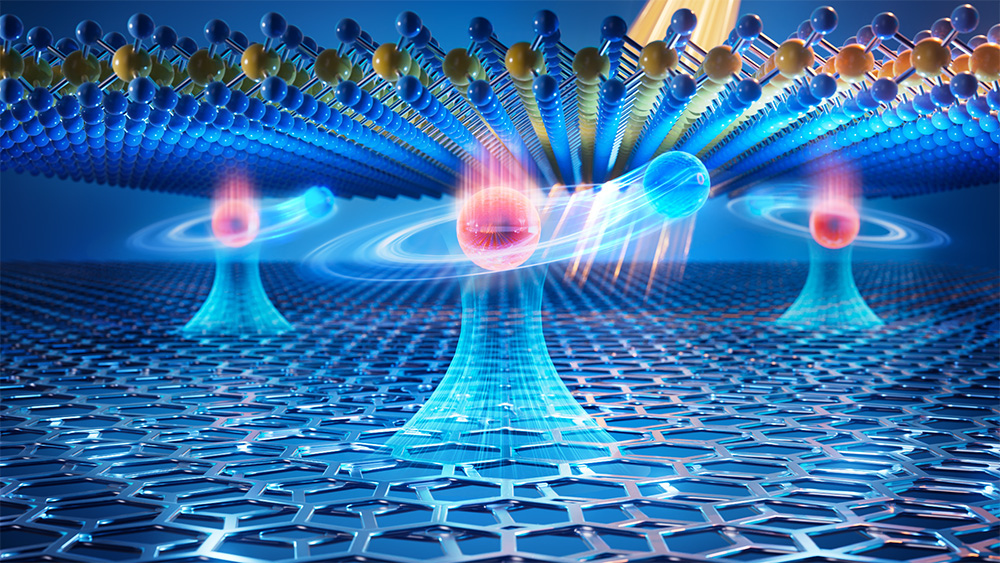 |
| An illustration exhibiting the Rydberg moiré excitons within the WSe2/TBG heterostructure. (Picture: IOP)
|
|
The solid-state nature of Rydberg excitons, their vital dipole moments, strong mutual interactions, and heightened interactions with the atmosphere counsel potential purposes in sensing, quantum optics, and quantum simulation. Nevertheless, the complete capability of Rydberg excitons has not been realized as a consequence of difficulties in effectively trapping and manipulating them. The introduction of two-dimensional (2D) moiré superlattices with tunable periodic potentials may present an answer.
|
|
In recent times, Dr. XU Yang and his colleagues have been investigating the usage of Rydberg excitons in 2D semiconducting transition steel dichalcogenides (like WSe2). They’ve developed a Rydberg sensing approach that leverages the sensitivity of Rydberg excitons to the dielectric atmosphere for detecting unique phases in close by 2D digital techniques.
|
|
Within the examine, the researchers used low-temperature optical spectroscopy measurements to detect Rydberg moiré excitons, as evidenced by a number of vitality splittings, a notable purple shift, and a narrowed linewidth within the reflectance spectra.
|
|
By way of numerical calculations by the workforce from Wuhan College, the findings had been linked to the spatially various cost distribution in TBG. This leads to a periodic potential panorama (known as moiré potential) for interplay with Rydberg excitons.
|
|
Sturdy confinement of Rydberg excitons was achieved as a consequence of unequal interlayer interactions of the constituent electron and gap of a Rydberg exciton. This was a results of spatially accrued prices within the AA-stacked areas of TBG. This course of results in Rydberg moiré excitons exhibiting electron-hole separation and the properties of long-lived charge-transfer excitons.
|
|
The workforce demonstrated a brand new methodology of manipulating Rydberg excitons, which is difficult in bulk semiconductors. The long-wavelength (tens of nm) moiré superlattice on this examine is much like optical lattices created by a standing-wave laser beam or optical tweezer arrays used for Rydberg atom trapping.
|
|
Moreover, the system’s management was improved as a consequence of tunable moiré wavelengths, in-situ electrostatic gating, and an extended lifetime. These options, mixed with robust light-matter interplay, facilitate optical excitation and readout.
|
|
This analysis may provide novel alternatives for additional Rydberg-Rydberg interactions and coherent management of Rydberg states, probably resulting in purposes in quantum data processing and quantum computation.
|