| Jul 06, 2023 |
|
(Nanowerk Information) Researchers within the Oregon State College Faculty of Science have demonstrated the potential of a reasonable nanomaterial to clean carbon dioxide from industrial emissions.
|
|
The findings, revealed in Cell Reviews Bodily Science (“CO2 seize from moist flue fuel utilizing a water-stable and cost-effective metal-organic framework”), are necessary as a result of improved carbon seize strategies are a key to addressing local weather change, mentioned OSU’s Kyriakos Stylianou, who led the research.
|
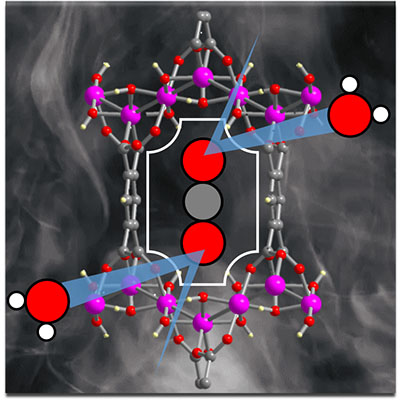 |
| The MOF in query. (Picture: OSU)
|
|
Carbon dioxide, a greenhouse fuel, outcomes from burning fossil fuels and is without doubt one of the major causes of a warming local weather.
|
|
Services that filter carbon from the air are starting to spring up across the globe – the world’s largest opened in 2021 in Iceland – however they’re not able to make a big dent within the worldwide emissions drawback, Stylianou notes. In a yr, the Iceland plant can draw out a carbon dioxide quantity equal to the annual emissions of about 800 vehicles.
|
|
Nevertheless, applied sciences for mitigating carbon dioxide on the level of entry into the ambiance, corresponding to a manufacturing facility, are comparatively effectively developed. A type of applied sciences includes nanomaterials generally known as steel natural frameworks, or MOFs, that may intercept carbon dioxide molecules by adsorption as flue gases make their manner by smokestacks.
|
|
“The seize of carbon dioxide is important for assembly net-zero emission targets,” mentioned Stylianou, an assistant professor of chemistry. “MOFs have proven a variety of promise for carbon seize due to their porosity and their structural versatility, however synthesizing them usually means utilizing reagents which can be expensive each economically and environmentally, corresponding to heavy steel salts and poisonous solvents.”
|
|
As well as, coping with the water portion of smokestack gases vastly complicates eradicating the carbon dioxide, he mentioned. Many MOFs which have proven carbon seize potential misplaced their effectiveness in humid situations. Flue gases could be dried, Stylianou mentioned, however that provides vital expense to the carbon dioxide removing course of, sufficient to make it nonviable for industrial purposes.
|
|
“So we sought to give you a MOF to deal with the assorted limitations of the supplies at the moment utilized in carbon seize: excessive price, poor selectivity for carbon dioxide, low stability in humid situations, and low CO2 uptake capacities,” he mentioned.
|
|
MOFs are crystalline, porous supplies made up of positively charged steel ions surrounded by natural “linker” molecules generally known as ligands. The steel ions make nodes that bind the linkers’ arms to kind a repeating construction that appears one thing like a cage; the construction has nanosized pores that adsorb gases, much like a sponge.
|
|
MOFs could be designed with a wide range of elements, which decide the MOF’s properties, and there are tens of millions of attainable MOFs, Stylianou mentioned. Virtually 100,000 of them have been synthesized by chemistry researchers, and the properties of one other half-million have been predicted.
|
|
“On this research we introduce a MOF composed of aluminum and a available ligand, benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylic acid,” Stylianou mentioned. “The synthesis of the MOF occurs in water and solely takes a few hours. And the MOF has pores with a dimension akin to that of CO2 molecules, which means there’s a confined area for incarcerating the carbon dioxide.”
|
|
The MOF works effectively in damp situations and in addition prefers carbon dioxide to nitrogen, which is necessary as a result of nitrogen oxides are an ingredient in flue gasses. With out that selectivity, the MOF would doubtlessly be binding to the fallacious molecules.
|
|
“This MOF is an impressive candidate for moist post-combustion carbon seize purposes,” Stylianou mentioned. “It’s price efficient with distinctive separation efficiency and could be regenerated and reused not less than 3 times with comparable uptake capacities.”
|

