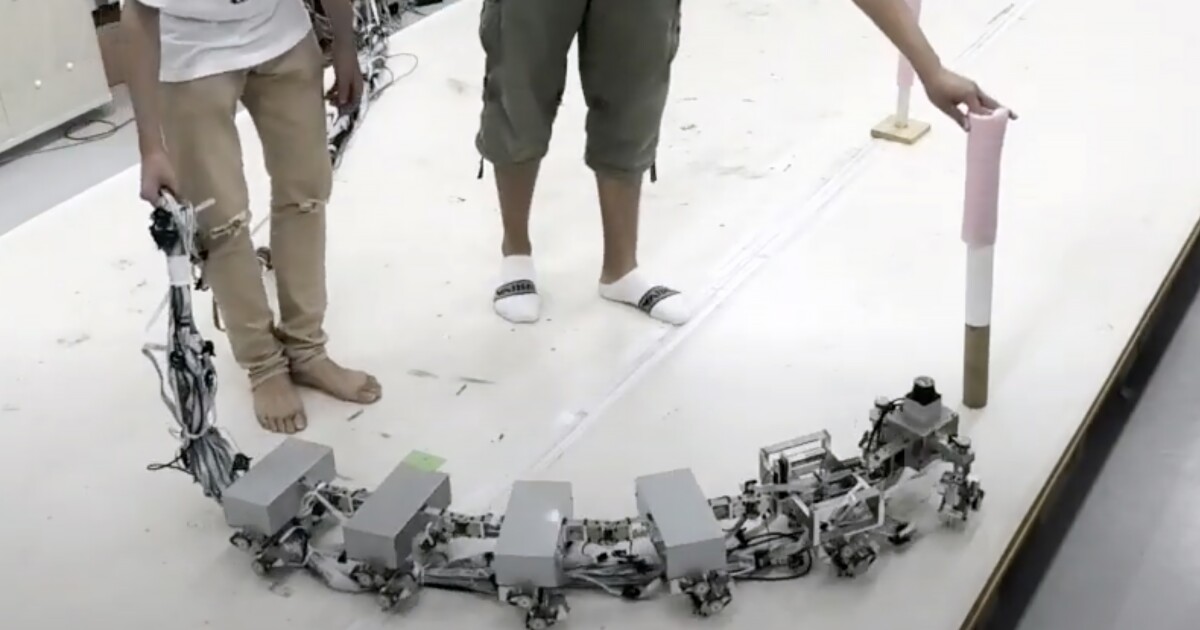
As soon as once more, expertise has been impressed by nature. After inspecting how centipedes traverse tough terrain, researchers created a multi-legged robotic that mimics their curved, side-to-side motion, offering better stability and maneuverability.
Centipedes and millipedes are myriapods, animals with elongated our bodies made up of quite a few comparable segments, practically all of which have jointed legs hooked up. Centipedes can transfer successfully in numerous terrain as a result of their versatile our bodies and the variety of limbs enable them to adapt their form to the surroundings.
Researchers making an attempt to create biomimetic multi-legged robots have usually discovered that they battle. When one leg malfunctions because of repeated stress, it could actually restrict the robotic’s skill to maneuver. And controlling a giant variety of legs requires quite a lot of pc energy. Now, researchers from Osaka College in Japan developed their very own robotic myriapod with six segments, every containing two legs, and versatile joints.
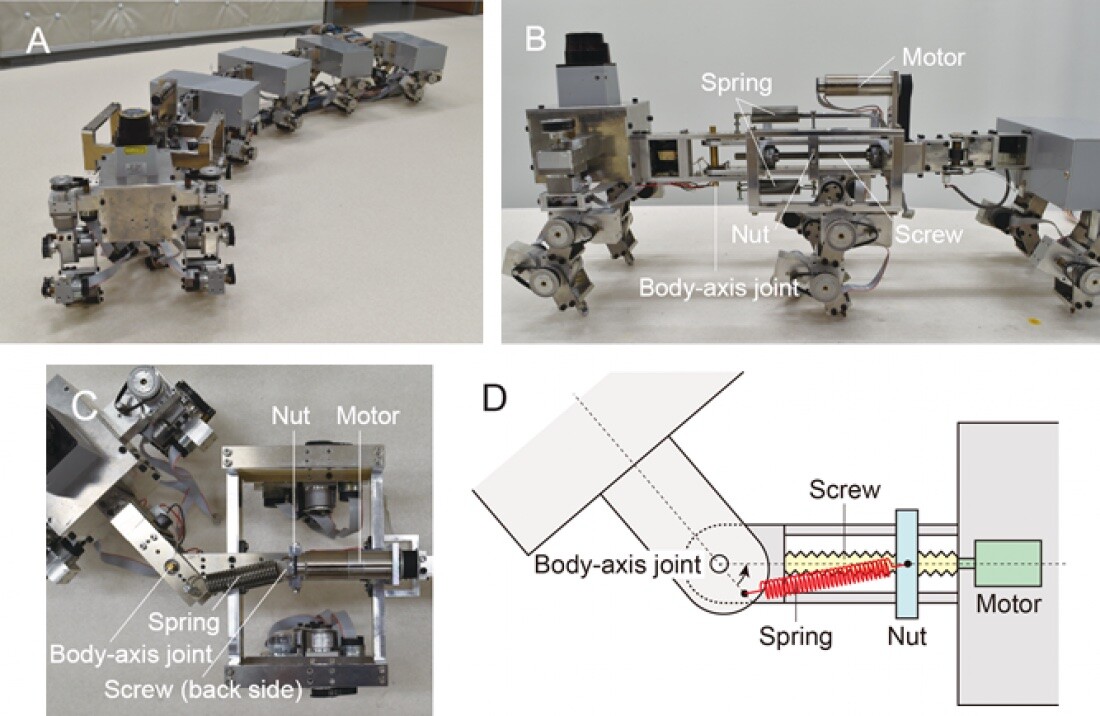
The robotic is 53 in (135 cm) in size and weighs 20 lb (9.1 kg). Its six separate segments have a pair of legs hooked up consisting of two hyperlinks linked by versatile joints that enable for yaw or motion in numerous instructions.
The researchers discovered that rising joint flexibility led to ‘pitchfork bifurcation,’ the place straight strolling turns into unstable. As an alternative of correcting the instability, the researchers ran with it, permitting the robotic to stroll in a curved sample, both to the left or the best, identical to a centipede would.
“We had been impressed by the power of sure extraordinarily agile bugs that permits them to regulate the dynamic instability in their very own movement to induce fast motion modifications,” mentioned Shinya Aoi, lead creator of the research.
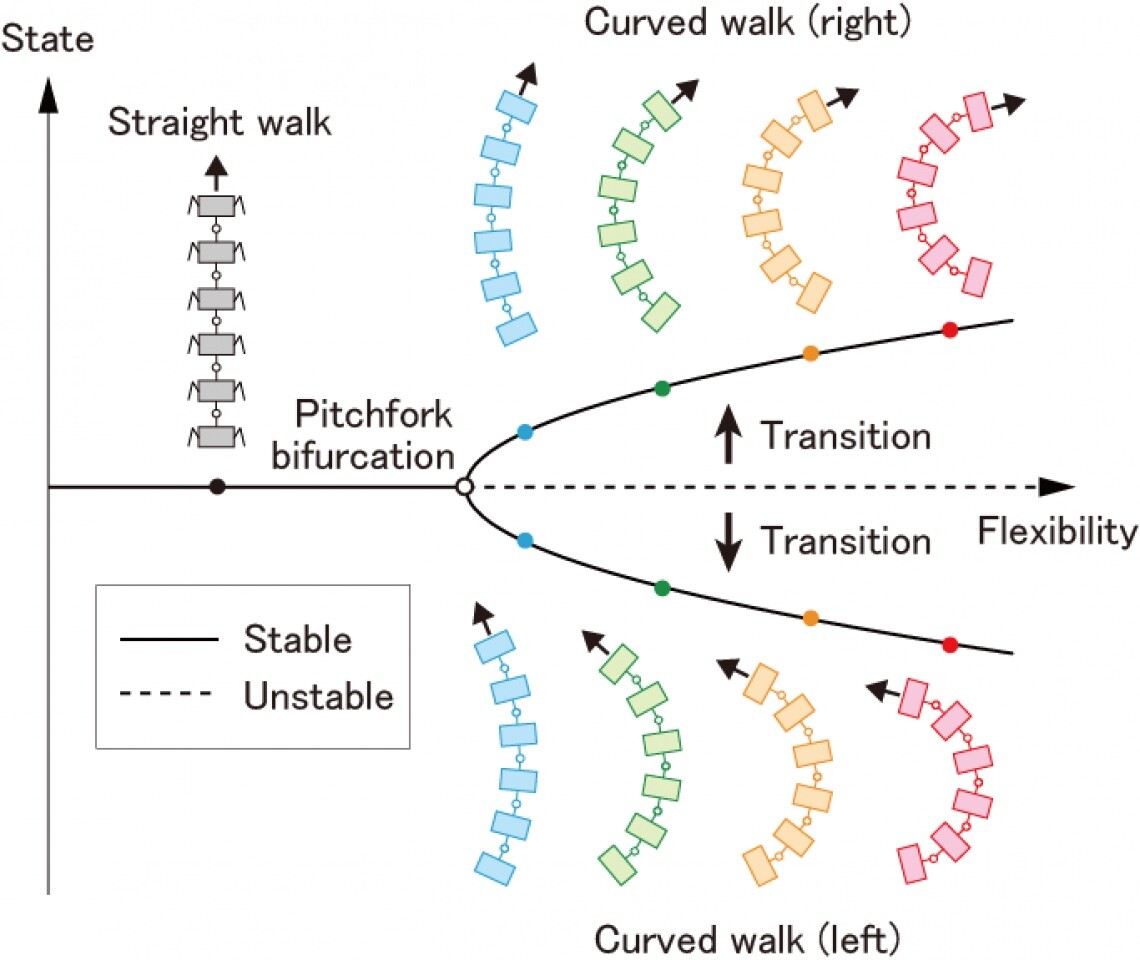
The researchers discovered that circuitously steering the robotic however, as a substitute, controlling its body-axis flexibility vastly lowered the computational complexity and the vitality necessities wanted to function the robotic.
After testing the robotic’s motion, they discovered that it might make its strategy to a goal by way of a curved path. The researchers see many functions for his or her robotic myriapod.
“We will foresee functions in all kinds of situations, akin to search and rescue, working in hazardous environments or exploration of different planets,” mentioned Mau Adachi, one of many research’s co-authors.
In future, the researchers plan to check their design in tougher environments, akin to on tough terrain.
The research was printed within the journal Mushy Robotics, and the under video, by the lead creator, Shinya Aoi, demonstrates the robotic’s maneuverability in reaching set targets.
Myriapod robotic with variable body-axis flexibility
Supply: Osaka College