| Sep 14, 2023 |
|
|
|
(Nanowerk Information) The speed at which the universe is increasing, often called the Hubble fixed, is likely one of the elementary parameters for understanding the evolution and supreme destiny of the cosmos. Nonetheless, a persistent distinction known as the “Hubble Stress” is seen between the worth of the fixed measured with a variety of unbiased distance indicators and its worth predicted from the massive bang afterglow.
|
|
NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope gives new capabilities to scrutinize and refine a number of the strongest observational proof for this stress. Nobel Laureate Adam Riess from the Johns Hopkins College and the Area Telescope Science Institute presents his and his colleagues’ current work utilizing Webb observations to enhance the precision of native measurements of the Hubble fixed.
|
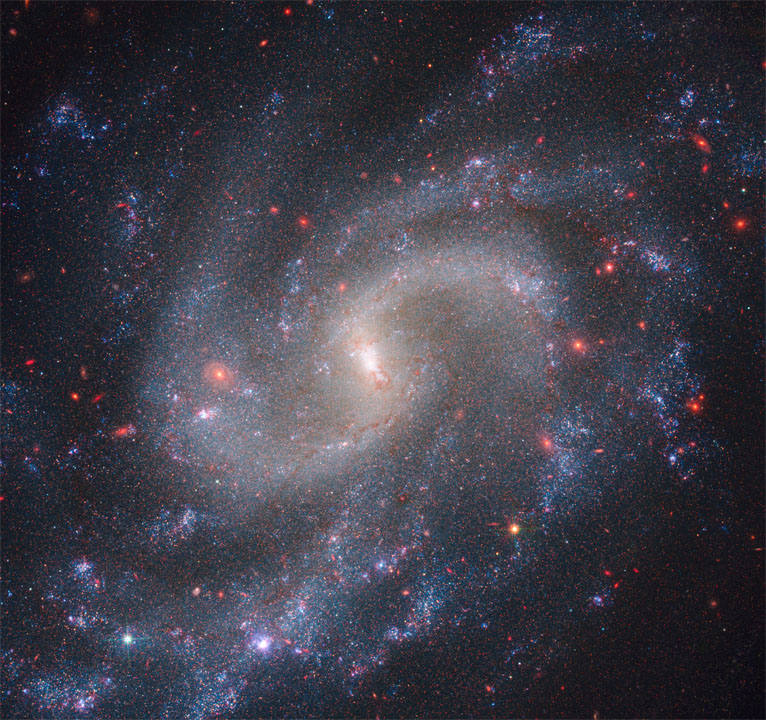 |
| Mixed observations from NASA’s NIRCam (Close to-Infrared Digital camera) and Hubble’s WFC3 (Vast Area Digital camera 3) present spiral galaxy NGC 5584, which resides 72 million light-years away from Earth. Amongst NGC 5584’s glowing stars are pulsating stars known as Cepheid variables and Kind Ia supernova, a particular class of exploding stars. Astronomers use Cepheid variables and Kind Ia supernovae as dependable distance markers to measure the universe’s growth price. (Picture: NASA, ESA, CSA, and A. Riess, STScI).
|
|
“Did you ever wrestle to see an indication that was on the fringe of your imaginative and prescient? What does it say? What does it imply? Even with essentially the most highly effective telescopes, the ‘indicators’ astronomers need to learn seem so small that we wrestle too.
|
|
“The signal cosmologists need to learn is a cosmic velocity restrict signal that tells us how briskly the universe is increasing — a quantity known as the Hubble fixed. Our signal is written into the celebrities in distant galaxies. The brightnesses of sure stars in these galaxies inform us how far-off they’re and thus for a way a lot time this mild has been touring to succeed in us, and the redshifts of the galaxies inform us how a lot the universe expanded over that point, therefore telling us the growth price.
|
|
“A selected class of stars, Cepheid variables, has given us essentially the most exact measurements of distance for over a century as a result of these stars are terribly vibrant: They’re supergiant stars, 100 thousand instances the luminosity of the Solar. What’s extra, they pulsate (that’s, broaden and contract in measurement) over a interval of weeks that signifies their relative luminosity. The longer the interval, the intrinsically brighter they’re. They’re the gold customary software for the aim of measuring the distances of galaxies 100 million or extra mild years away, a vital step to find out the Hubble fixed. Sadly, stars in galaxies are crowded collectively in a small house from our distant vantage level and so we frequently lack the decision to separate them from their line-of-sight neighbors.
|
|
“A serious justification for constructing the Hubble Area Telescope was to resolve this drawback. Previous to Hubble’s 1990 launch and its subsequent Cepheid measurements, the growth price of the universe was so unsure astronomers weren’t certain if the universe has been increasing for 10 billion or 20 billion years. That’s as a result of a quicker growth price will result in a youthful age for the universe, and a slower growth price will result in an older age of the universe. Hubble has higher visible-wavelength decision than any ground-based telescope as a result of it sits above the blurring results of Earth’s environment. Because of this, it could establish particular person Cepheid variables in galaxies which might be greater than 100 million light-years away and measure the time interval over which they modify their brightness.
|
|
“Nonetheless, we additionally should observe the Cepheids on the near-infrared a part of the spectrum to see the sunshine which passes unscathed by means of intervening mud. (Mud absorbs and scatters blue optical mild, making distant objects look faint and fooling us into believing they’re farther away than they’re). Sadly, Hubble’s red-light imaginative and prescient isn’t as sharp as its blue, so the Cepheid starlight we see there may be blended with different stars in its discipline of view. We are able to account for the typical quantity of mixing, statistically, the identical manner a health care provider figures out your weight by subtracting the typical weight of garments from the size studying, however doing so provides noise to the measurements. Some individuals’s garments are heavier than others.
|
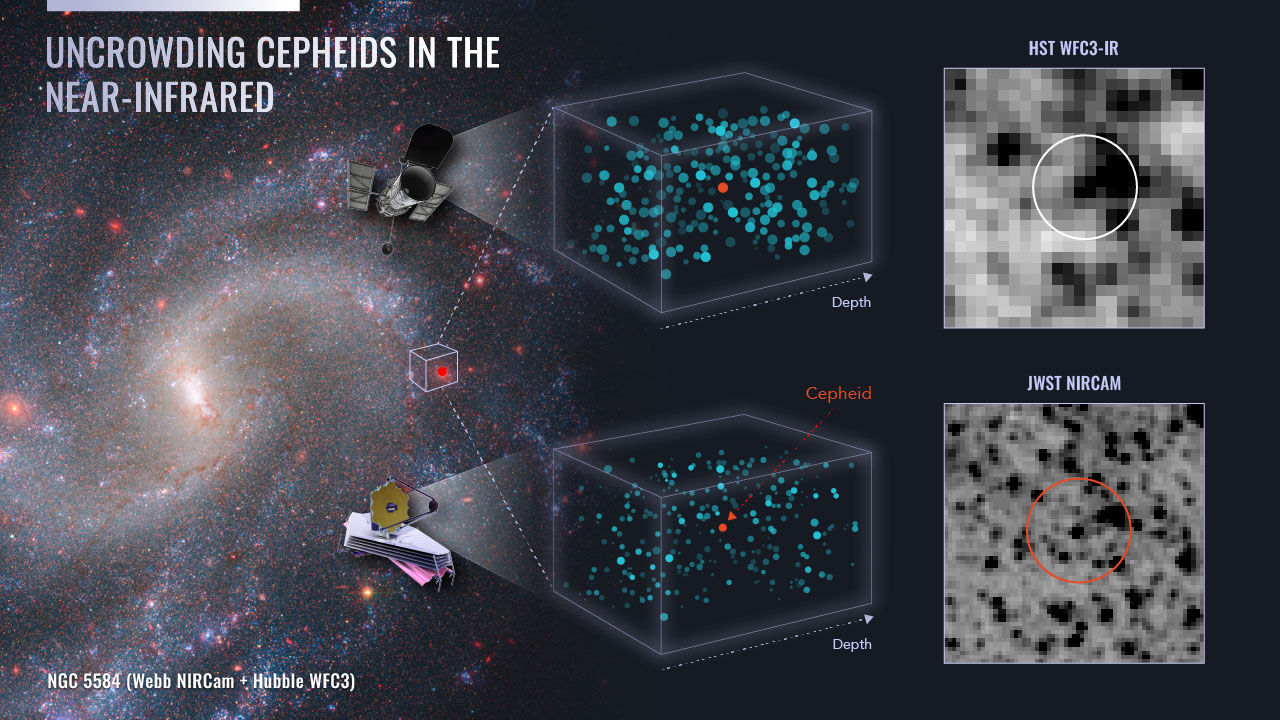 |
| This diagram illustrates the mixed energy of the NASA’s Hubble and Webb house telescopes in nailing down exact distances to a particular class of variable star that’s utilized in calibrating the growth price of the universe. These Cepheid variable stars are seen in crowded star fields. Gentle contamination from surrounding stars might make the measurement of the brightness of a Cepheid much less exact. Webb’s sharper infrared imaginative and prescient permits for a Cepheid goal to be extra clearly remoted from surrounding stars, as seen in the fitting facet of the diagram. The Webb knowledge confirms the accuracy of 30 years of Hubble observations of Cepheids that have been essential in establishing the underside rung of the cosmic distance ladder for measuring the universe’s growth price. On the left, NGC 5584 is seen in a composite picture from Webb’s NIRCam (Close to-Infrared Digital camera) and Hubble’s Vast Area Digital camera 3. (Picture: NASA, ESA, A. Riess (STScI), W. Yuan (STScI)). (click on on picture to enlarge)
|
|
“Nonetheless, sharp infrared imaginative and prescient is likely one of the James Webb Area Telescope’s superpowers. With its massive mirror and delicate optics, it could readily separate the Cepheid mild from neighboring stars with little mixing. Within the first 12 months of Webb operations with our Common Observers program 1685, we collected observations of Cepheids discovered by Hubble at two steps alongside what’s often called the cosmic distance ladder. Step one entails observing Cepheids in a galaxy with a identified, geometric distance that enables us to calibrate the true luminosity of Cepheids. For our program that galaxy is NGC 4258. The second step is to look at Cepheids within the host galaxies of current Kind Ia supernovae. The mix of the primary two steps transfers data of the space to the supernovae to calibrate their true luminosities. Step three is to look at these supernovae far-off the place the growth of the universe is obvious and might be measured by evaluating the distances inferred from their brightness and the redshifts of the supernova host galaxies. This sequence of steps is named the space ladder.
|
|
“We not too long ago received our first Webb measurements from steps one and two which permits us to finish the space ladder and evaluate to the earlier measurements with Hubble (see determine) Webb’s measurements have dramatically reduce the noise within the Cepheid measurements because of the observatory’s decision at near-infrared wavelengths. This type of enchancment is the stuff astronomers dream of! We noticed greater than 320 Cepheids throughout the primary two steps. We confirmed that the sooner Hubble Area Telescope measurements have been correct, albeit noisier. We’ve got additionally noticed 4 extra supernova hosts with Webb and we see an identical outcome for the entire pattern.
|
|
“What the outcomes nonetheless don’t clarify is why the universe seems to be increasing so quick! We are able to predict the growth price of the universe by observing its child image, the cosmic microwave background, after which using our greatest mannequin of the way it grows up over time to inform us how briskly the universe ought to be increasing as we speak. The truth that the current measure of the growth price considerably exceeds the prediction is a now decade-long drawback known as “The Hubble Stress.” Essentially the most thrilling chance is that the Stress is a clue about one thing we’re lacking in our understanding of the cosmos.
|
|
“It might point out the presence of unique darkish vitality, unique darkish matter, a revision to our understanding of gravity, or the presence of a novel particle or discipline. The extra mundane clarification could be a number of measurement errors conspiring in the identical course (astronomers have dominated out a single error by utilizing unbiased steps), so that’s the reason it’s so essential to redo the measurements with larger constancy. With Webb confirming the measurements from Hubble, the Webb measurements present the strongest proof but that systematic errors in Hubble’s Cepheid photometry don’t play a major function within the current Hubble Stress. Because of this, the extra attention-grabbing potentialities stay on the desk and the thriller of the Stress deepens.”
|
|
The James Webb Area Telescope is the world’s largest, strongest, and most advanced house science telescope ever constructed. Webb will clear up mysteries in our photo voltaic system, look past to distant worlds round different stars, and probe the mysterious constructions and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is a world program led by NASA with its companions, ESA (European Area Company) and the Canadian Area Company.
|
|
This text highlights knowledge from a paper that was accepted by The Astrophysical Journal (“Crowded No Extra: The Accuracy of the Hubble Fixed Examined with Excessive Decision Observations of Cepheids by JWST”).
|



