The non-public cloud, as we all know it, first got here onto the scene in 2010 when corporations like Microsoft, AWS and OpenStack developed non-public clouds that have been fairly useful. That is additionally when OpenStack created an open-source, do-it-yourself and free cloud.
On this article, we outline non-public cloud and clarify the way it works, noting the advantages and drawbacks. We offer you a complete understanding of personal cloud, enabling you to make knowledgeable choices about its relevance and applicability to your group.
Leap to:
What’s a non-public cloud?
A personal cloud is a single-tenant surroundings, that means just one group makes use of the infrastructure and instantly controls it. It’s considered one of three essential cloud deployment fashions — non-public, public and hybrid. There’s additionally multicloud, which mixes parts of all three.
SEE: Discover the advantages and disadvantages of a hybrid cloud setup.
A personal cloud could be hosted and managed in numerous methods, together with using sources and infrastructure which are already on-premises, using separate infrastructure offered by a third-party group or being enabled solely utilizing virtualization software program.
How does the non-public cloud work?
A personal cloud dedicates particular cloud sources to a single group or tenant, making certain a excessive stage of safety and privateness by means of a proprietary structure. Both the group itself or a third-party service manages this structure.
The group’s intranet or a hosted information heart homes the non-public cloud infrastructure, the place a non-public community maintains companies and infrastructure. This setup supplies the group with higher management over information, improved safety, and the pliability to customise {hardware} and software program to fulfill particular enterprise wants.
As well as, firewall know-how protects the information saved in a non-public cloud, and inner internet hosting ensures the group retains management over delicate info.
Forms of non-public clouds
Personal clouds differ in internet hosting and administration and supply various capabilities relying on the group’s wants. There are 4 essential varieties of non-public clouds:
- On-premises: On-premises non-public clouds are owned and managed by the group, usually utilizing its personal {hardware} and software program. It presents the best stage of management and customization but additionally requires important sources for setup and upkeep.
- Hosted: Hosted non-public clouds, often known as non-public cloud internet hosting, are offered by a third-party vendor the place the {hardware} and software program are owned and managed by the supplier. This feature could be cheaper however might not supply the identical stage of customization and management as an on-premises non-public cloud.
- Managed: In managed non-public clouds, the {hardware} and software program are owned by the group however managed by a third-party vendor. This presents a stability between customization and management and value financial savings.
- Digital: Digital non-public clouds supply organizations entry to public cloud sources whereas sustaining privateness and management by means of digital non-public community know-how.
Nevertheless, the above solely categorizes non-public cloud when it comes to internet hosting and administration. Different classifications contemplate the cloud infrastructure used:
- Software program-only: This non-public cloud makes use of software program to handle and deploy virtualized sources however doesn’t use devoted {hardware}, and it presents decrease upfront prices however might have much less scalability because of the lack of devoted {hardware}.
- Software program and {hardware}: This non-public cloud makes use of each software program and devoted {hardware} for administration and deployment, providing higher scalability but additionally greater preliminary prices.
Advantages of personal clouds
Personal clouds supply a bunch of advantages when in comparison with public cloud options.
Customization and management
Maybe most significantly, non-public clouds ship greater ranges of customization and management. It’s because non-public cloud environments aren’t shared with different organizations in the best way public clouds are. In consequence, non-public cloud customers can configure their functions and programs to fulfill their particular wants and necessities.
SEE: TechRepublic Premium’s cloud engineer hiring equipment has the whole lot you’ll want to discover the appropriate individual in your engineering crew.
Safety and compliance
As well as, non-public cloud options supply higher safety and compliance with sure laws. For organizations that deal with delicate information, non-public clouds can present an additional layer of safety.
A personal cloud could be configured to fulfill these laws, offering an audit path for compliance functions. That is usually tougher in a multicloud or hybrid cloud setup, the place information could also be saved in several places and topic to totally different jurisdictions.
Mission crucial workloads
Personal clouds are sometimes deployed when public clouds are deemed inappropriate or insufficient. For instance, mission-critical workloads exceeding danger tolerance ranges could also be higher suited to non-public clouds.
Drawbacks of personal clouds
Personal clouds have gotten more and more common as companies search for methods to enhance effectivity and management prices. Nevertheless, non-public clouds include a variety of disadvantages, which have led to a gradual shift to multicloud setups.
Elevated complexity
Personal clouds require a big funding in {hardware} and software program and cautious planning and administration. As well as, the elevated complexity may imply that corporations with out skilled cloud engineers can face the identical drawback that public cloud prospects encounter with poor configuration, provisioning and overburdened servers.
Much less scalable and versatile
Personal clouds could be much less scalable than public clouds, making them much less in a position to cope with spikes in demand. Scalability requires important funding in extra {hardware} and software program in non-public cloud setup. This may be time-consuming and expensive.
Personal clouds may also be extra rigid, that means organizations utilizing a non-public cloud gained’t be capable to shortly adapt to adjustments in know-how, enterprise wants or market circumstances. Furthermore, adjustments to personal cloud infrastructure could be advanced and require important funding, particularly the place new know-how is incompatible with current infrastructure.
Excessive prices
One of many essential drawbacks of personal clouds is the preliminary funding required for acquisition, deployment and help. For instance, an organization might want to buy costly {hardware} and software program in addition to rent employees with the mandatory experience to take care of and help the system.
Additional, subscription prices of hosted non-public cloud can typically exceed the price of whole possession.
Personal cloud pricing
A number of components decide the price of non-public cloud:
- {Hardware} and infrastructure: The price of the bodily servers, storage and networking tools wanted to arrange a non-public cloud could be substantial, particularly for on-premises options, which additionally consists of the price of the information heart house, energy and cooling programs.
- Software program and licensing: Personal clouds require virtualization software program, cloud administration platforms and different software program instruments for operation, the price of which might add up over time.
- Administration and upkeep: Whether or not managed internally or outsourced to a third-party, the continuing administration and upkeep of a non-public cloud could be a important price issue. This consists of system updates, safety measures, troubleshooting and {hardware} alternative.
- Staffing: Expert IT personnel are wanted to handle and preserve the non-public cloud. This consists of salaries, advantages and coaching prices for these staff.
- Safety and compliance: Relying on the trade, there could also be extra prices related to assembly particular safety requirements and compliance laws. For example, the healthcare trade together with healthcare suppliers and enterprise associates within the U.S. should adjust to stringent HIPAA guidelines on information privateness and safety.
As regards pricing fashions, non-public cloud prices are usually structured in considered one of two methods:
- Capital expenditure mannequin: The group makes a big upfront funding to buy the {hardware} and software program wanted for the non-public cloud. The CapEx mannequin is widespread for on-premises non-public clouds. Whereas the preliminary price is excessive, the group has full management over its sources and may depreciate the belongings over time.
- Operational expenditure mannequin: The group pays an everyday charge to a third-party supplier for the usage of the non-public cloud infrastructure and related companies. This mannequin is widespread for hosted or managed non-public clouds. The OpEx mannequin permits for decrease upfront prices and higher flexibility, however the ongoing prices can add up over time.
Personal cloud safety
When configured accurately, non-public cloud presents a lot better safety because it dedicates its whole infrastructure to a single group, not like multicloud or hybrid cloud setups, the place sources are shared amongst a number of tenants. Due to this fact, with a non-public cloud setup, the group has full management over its information, lowering the chance of unauthorized entry or information breaches.
In a non-public cloud surroundings, the group can implement stringent safety insurance policies and controls tailor-made to its particular wants. This consists of:
- Superior firewalls.
- Intrusion detection programs.
- Encryption protocols for information at relaxation and in transit.
- Entry management and privileges.
Personal clouds additionally supply higher visibility and management over your entire infrastructure. In a multicloud or hybrid cloud setup, components of the infrastructure are managed by totally different suppliers, which might make it tough to observe and handle safety successfully. In distinction, a non-public cloud supplies a unified view of your entire infrastructure, making it simpler to detect and reply to potential safety threats.
Personal cloud suppliers
Some main non-public cloud suppliers embody Amazon Net Providers, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud and VMware. Every vendor presents a spread of personal cloud choices with various ranges of customization and management.
Ought to your group use a non-public cloud?
Based mostly on the benefits that non-public cloud presents, it might look like an apparent selection. There is just one drawback: price. The price of non-public cloud on each a CapEx or OpEx mannequin could be prohibitively excessive for many organizations, main them to implement hybrid, public or multicloud setups as a substitute.
In response to Flexera’s 2023 State of the Cloud report, solely 2% of 750 IT professionals surveyed use a single non-public cloud, with multicloud deployments being the de facto customary (Determine A).
Determine A
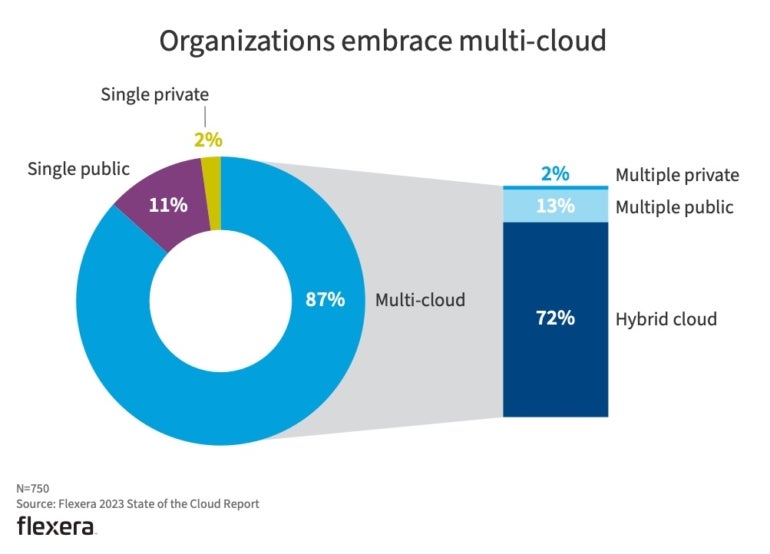
The Flexera report additionally emphasizes that managing cloud spend has overtaken safety as the highest problem going through organizations. This means that whereas price is a priority, the power to successfully handle and optimize that spend is equally vital.
A multicloud technique permits organizations to leverage the strengths of various cloud suppliers and keep away from vendor lock-in. This method can present price financial savings, flexibility and resilience. Nevertheless, it additionally requires cautious administration to make sure that sources are used effectively, and that safety is maintained throughout totally different platforms.
Given these concerns, it’s clear that the choice to make use of a non-public cloud shouldn’t be primarily based solely on price. As a substitute, organizations ought to contemplate their particular wants, together with their safety necessities, regulatory surroundings and the character of their workloads. For mission-critical functions and delicate information, a non-public cloud could also be the most suitable choice, regardless of the upper price.

