That is the fifth submit in a collection by Rockset’s CTO and Co-founder Dhruba Borthakur on Designing the Subsequent Era of Knowledge Techniques for Actual-Time Analytics. We’ll be publishing extra posts within the collection within the close to future, so subscribe to our weblog so you do not miss them!
Posts printed to date within the collection:
- Why Mutability Is Important for Actual-Time Knowledge Analytics
- Dealing with Out-of-Order Knowledge in Actual-Time Analytics Purposes
- Dealing with Bursty Visitors in Actual-Time Analytics Purposes
- SQL and Complicated Queries Are Wanted for Actual-Time Analytics
- Why Actual-Time Analytics Requires Each the Flexibility of NoSQL and Strict Schemas of SQL Techniques
The toughest substance on earth, diamonds, have surprisingly restricted makes use of: noticed blades, drilling bits, marriage ceremony rings and different industrial functions.
In contrast, one of many softer metals in nature, iron, may be reworked for an limitless checklist of functions: the sharpest blades, the tallest skyscrapers, the heaviest ships, and shortly, if Elon Musk is correct, the most cost-effective EV automotive batteries.
In different phrases, iron’s unbelievable usefulness is as a result of it’s each inflexible and versatile.
Equally, databases are solely helpful for as we speak’s real-time analytics if they are often each strict and versatile.
Conventional databases, with their wholly-inflexible constructions, are brittle. So are schemaless NoSQL databases, which capably ingest firehoses of knowledge however are poor at extracting complicated insights from that knowledge.
Buyer personalization, autonomic stock administration, operational intelligence and different real-time use circumstances require databases that stricly implement schemas and possess the flexibility to robotically redefine these schemas primarily based on the information itself. This satisfies the three key necessities of contemporary analytics:
- Assist each scale and pace for ingesting knowledge
- Assist versatile schemas that may immediately adapt to the range of streaming knowledge
- Assist quick, complicated SQL queries that require a strict construction or schema
Yesterday’s Schemas: Laborious however Fragile
The traditional schema is the relational database desk: rows of entities, e.g. folks, and columns of various attributes (age or gender) of these entities. Sometimes saved in SQL statements, the schema additionally defines all of the tables within the database and their relationship to one another.
Historically, schemas are strictly enforced. Incoming knowledge that doesn’t match the predefined attributes or knowledge sorts is robotically rejected by the database, with a null worth saved as an alternative or the complete document skipped utterly. Altering schemas was tough and barely executed. Corporations rigorously engineered their ETL knowledge pipelines to align with their schemas (not vice-versa).
There have been good causes again within the day for pre-creating and strictly imposing schemas. SQL queries have been simpler to jot down. In addition they ran so much quicker. Most significantly, inflexible schemas prevented question errors created by unhealthy or mismatched knowledge.
Nonetheless, strict, unchanging schemas have large disadvantages as we speak. First, there are various extra sources and kinds of knowledge than there have been within the 90s. A lot of them can’t simply match into the identical schema construction. Most notable are real-time occasion streams. Streaming and time-series knowledge often arrives in semi-structured codecs that change often. As these codecs change, so should the schemas.
Second, as enterprise situations change, corporations regularly want to research new knowledge sources, run various kinds of analytics – or just replace their knowledge sorts or labels.
Right here’s an instance. Again once I was on the information infrastructure workforce at Fb, we have been concerned in an formidable initiative referred to as Challenge Nectar. Fb’s person base was exploding. Nectar was an try to log each person motion with a regular set of attributes. Standardizing this schema worldwide would allow us to research traits and spot anomalies on a worldwide degree. After a lot inner debate, our workforce agreed to retailer each person occasion in Hadoop utilizing a timestamp in a column named time_spent that had a decision of a second.
After debuting Challenge Nectar, we introduced it to a brand new set of software builders. The primary query they requested: “Can you alter the column time-spent from seconds to milliseconds?” In different phrases, they casually requested us to rebuild a basic side of Nectar’s schema post-launch!
ETL pipelines can make all of your knowledge sources match underneath the identical proverbial roof (that’s what the T, which stands for knowledge transformation, is all about). Nonetheless, ETL pipelines are time-consuming and costly to arrange, function, and manually replace as your knowledge sources and kinds evolve.
Makes an attempt at Flexibility
Strict, unchanging schemas destroy agility, which all corporations want as we speak. Some database makers responded to this downside by making it simpler for customers to manually modify their schemas. There have been heavy tradeoffs, although.
Altering schemas utilizing the SQL ALTER-TABLE command takes a whole lot of time and processing energy, leaving your database offline for an prolonged time. And as soon as the schema is up to date, there’s a excessive danger of inadvertently corrupting your knowledge and crippling your knowledge pipeline.
Take PostgreSQL, the favored transactional database that many corporations have additionally used for easy analytics. To correctly ingest as we speak’s fast-changing occasion streams, PostgreSQL should change its schema by a handbook ALTER-TABLE command in SQL. This locks the database desk and freezes all queries and transactions for so long as ALTER-TABLE takes to complete. In line with many commentators, ALTER-TABLE takes a very long time, regardless of the dimension of your PostgreSQL desk. It additionally requires a whole lot of CPU, and creates the danger of knowledge errors and damaged downstream functions.
The identical issues face the NewSQL database, CockroachDB. CockroachDB guarantees on-line schema modifications with zero downtime. Nonetheless, Cockroach warns towards doing multiple schema change at a time. It additionally strongly cautions towards altering schemas throughout a transaction. And identical to PostgreSQL, all schema modifications in CockroachDB have to be carried out manually by the person. So CockroachDB’s schemas are far much less versatile than they first seem. And the identical danger of knowledge errors and knowledge downtime additionally exists.
NoSQL Involves the Rescue … Not
Different makers launched NoSQL databases that enormously relaxed schemas or deserted them altogether.
This radical design alternative made NoSQL databases — doc databases, key-value shops, column-oriented databases and graph databases — nice at storing large quantities of knowledge of various sorts collectively, whether or not it’s structured, semi-structured or polymorphic.
Knowledge lakes constructed on NoSQL databases equivalent to Hadoop are the very best instance of scaled-out knowledge repositories of blended sorts. NoSQL databases are additionally quick at retrieving massive quantities of knowledge and operating easy queries.
Nonetheless, there are actual disadvantages to light-weight/no-weight schema databases.
Whereas lookups and easy queries may be quick and straightforward, queries which can be complicated. nested and should return exact solutions are likely to run slowly and be tough to create. That’s as a result of lack of SQL help, and their tendency to poorly help indexes and different question optimizations. Complicated queries are much more more likely to trip with out returning outcomes as a result of NoSQL’s overly-relaxed knowledge consistency mannequin. Fixing and rerunning the queries is a time-wasting trouble. And in the case of the cloud and builders, which means wasted cash.
Take the Hive analytics database that’s a part of the Hadoop stack. Hive does help versatile schemas, however crudely. When it encounters semi-structured knowledge that doesn’t match neatly into its current tables and databases, it merely shops the information as a JSON-like blob. This retains the information intact. Nonetheless, at question time, the blobs must be deserialized first, a gradual and inefficient course of.
Or take Amazon DynamoDB, which makes use of a schemaless key-value retailer. DynamoDB is ultra-fast at studying particular data. Multi-record queries are typically a lot slower, although constructing secondary indexes will help. The larger difficulty is that DynamoDB doesn’t help any JOINs or every other complicated queries.
The Proper Strategy to Strict and Versatile Schemas
There’s a successful database system, nonetheless, that blends the versatile scalability of NoSQL with the accuracy and reliability of SQL, whereas including a splash of the low-ops simplicity of cloud-native infrastructure.
Rockset is a real-time analytics platform constructed on high of the RocksDB key-value retailer. Like different NoSQL databases, Rockset is extremely scalable, versatile and quick at writing knowledge. However like SQL relational databases, Rockset has the benefits of strict schemas: sturdy (however dynamic) knowledge sorts and excessive knowledge consistency, which, together with our automated and environment friendly Converged Indexing™, mix to make sure your complicated SQL queries are quick.
Rockset robotically generates schemas by inspecting knowledge for fields and knowledge sorts as it’s saved. And Rockset can deal with any kind of knowledge thrown at it, together with:
- JSON knowledge with deeply-nested arrays and objects, in addition to blended knowledge sorts and sparse fields
- Actual-time occasion streams that consistently add new fields over time
- New knowledge sorts from new knowledge sources
Supporting schemaless ingest together with Converged Indexing permits Rockset to scale back knowledge latency by eradicating the necessity for upstream knowledge transformations.
Rockset has different optimization options to scale back storage prices and speed up queries. For each area of each document, Rockset shops the information kind. This maximizes question efficiency and minimizes errors. And we do that effectively by a characteristic referred to as area interning that reduces the required storage by as much as 30 % in comparison with a schemaless JSON-based doc database, for instance.
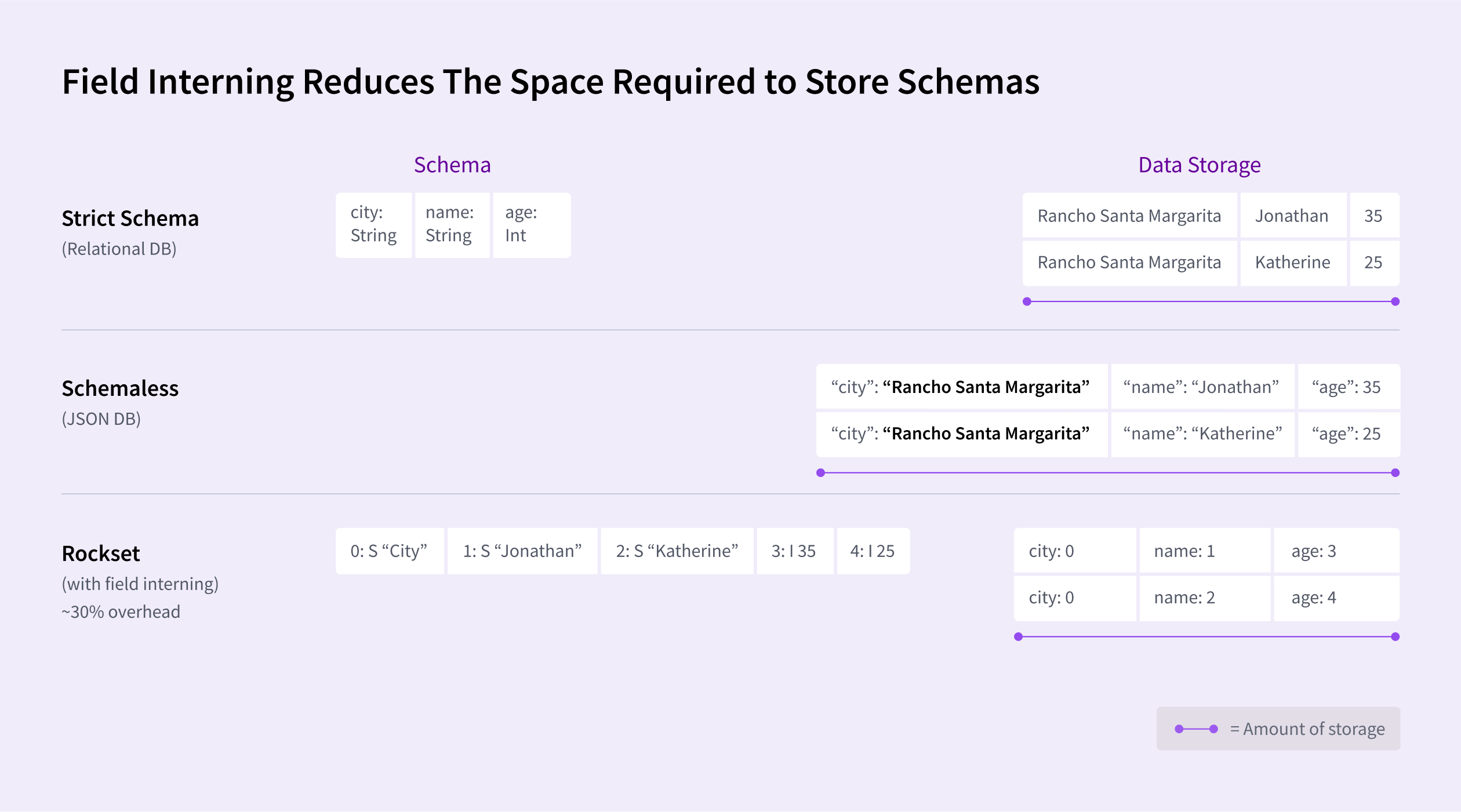
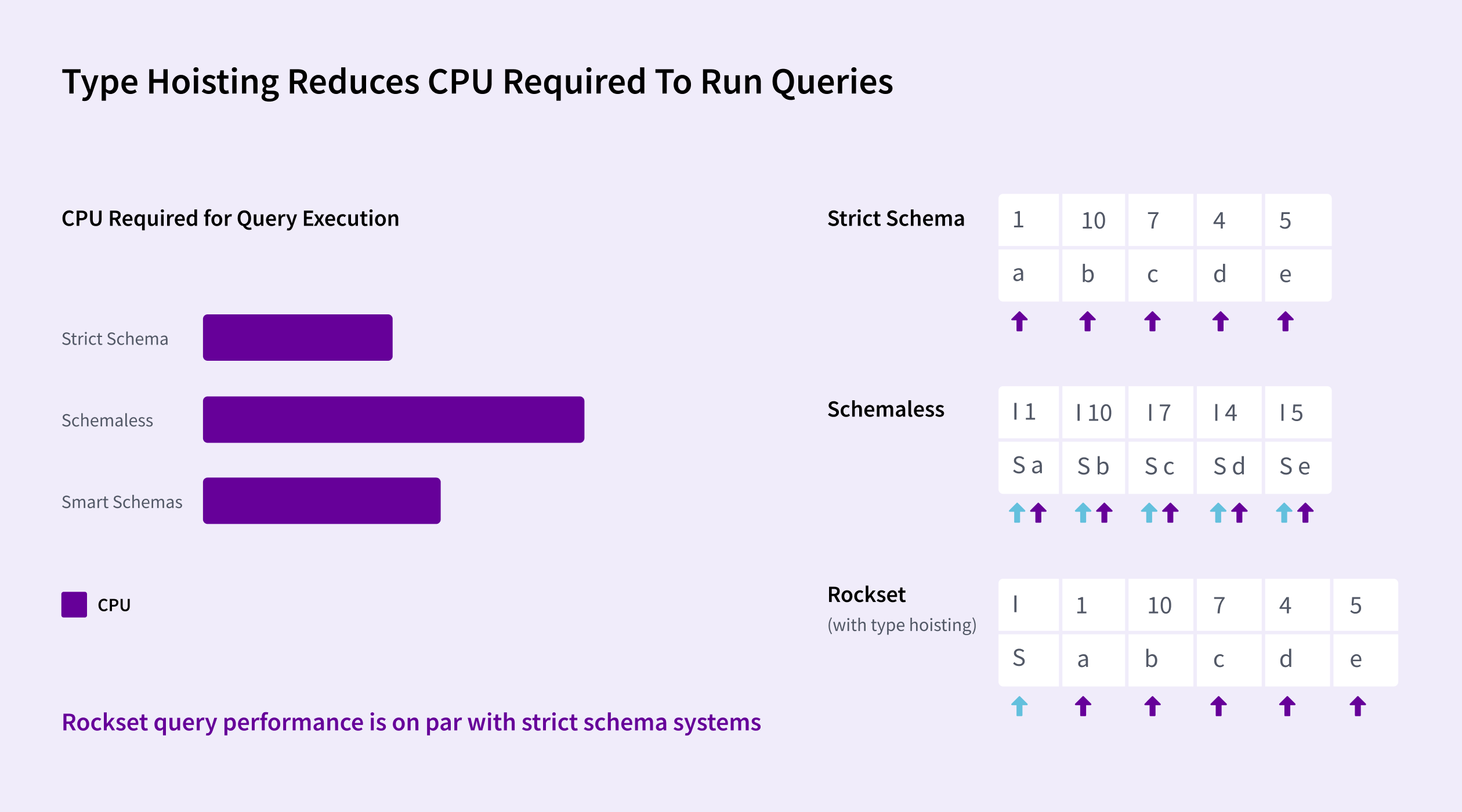
Rockset makes use of one thing referred to as kind hoisting that reduces processing time for queries. Adjoining gadgets which have the identical kind can hoist their kind data to use to the complete set of things quite than storing with each particular person merchandise within the checklist. This permits vectorized CPU directions to course of the complete set of things rapidly. This implementation – together with our Converged Index™ – permits Rockset queries to run as quick as databases with inflexible schemas with out incurring extra compute.
Some NoSQL database makers declare solely they’ll help versatile schemas nicely. It is not true and is only one of many outdated knowledge myths that fashionable choices equivalent to Rockset are busting.
I invite you to study extra about how Rockset’s structure gives the very best of conventional and fashionable — SQL and NoSQL — schemaless knowledge ingestion with automated schematization. This structure totally empowers complicated queries and can fulfill the necessities of the most demanding real-time knowledge functions with stunning effectivity.

