| Jun 01, 2023 |
|
|
|
(Nanowerk Information) Human pores and skin is superb. It senses temperature, stress, and texture. It’s in a position to stretch and spring again, again and again. And it offers a barrier between the physique and dangerous issues on the earth—micro organism, viruses, toxins, ultraviolet radiation and extra. Engineers are, accordingly, eager to create artificial pores and skin. They think about robots and prosthetic limbs which have skin-like qualities—not the least of which is pores and skin’s outstanding capacity to heal.
|
|
“We’ve achieved what we consider to be the primary demonstration of a multi-layer, skinny movie sensor that routinely realigns throughout therapeutic. This can be a vital step towards mimicking human pores and skin, which has a number of layers that each one re-assemble accurately throughout the therapeutic course of,” mentioned Chris Cooper, a Ph.D. candidate at Stanford College who, together with postdoctoral researcher Sam Root, is co-author of a brand new research in Science saying the advance (“Autonomous alignment and therapeutic in multilayer smooth electronics utilizing immiscible dynamic polymers”).
|
|
Layering is vital to mimicking pores and skin’s many qualities. “It’s smooth and stretchable. However should you puncture it, slice it, or lower it— every layer will selectively heal with itself to revive the general operate,” Root says. “Similar to actual pores and skin.”
|
|
Pores and skin, too, is shaped of layers. It has simply developed immune mechanisms that rebuild the tissue with the unique layered construction by a posh course of involving molecular recognition and signaling.
|
|
“With true ‘pores and skin’ the layers ought to realign naturally and autonomously,” Cooper says.
|
|
Root says the crew, led by Professor Zhenan Bao at Stanford College, would possibly be capable to create multi-tiered artificial pores and skin with individually practical layers as skinny as a micron every, maybe much less. Skinny sufficient {that a} stack of 10 or extra layers can be no thicker than a sheet of paper. “One layer would possibly sense stress, one other temperature, and one more rigidity,” says Root. The fabric of various layers could be engineered to sense thermal, mechanical, or electrical adjustments.
|
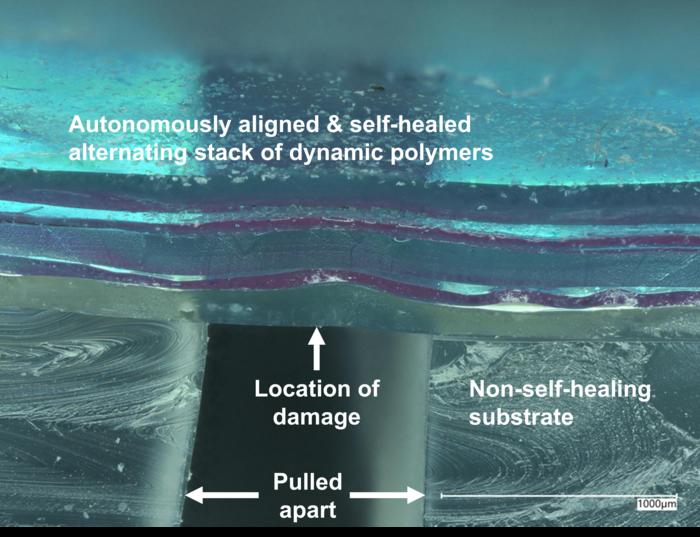 |
| A depth-profiled digital microscope {photograph} of a 5-layer alternating laminate movie of immiscible dynamic polymer movies which have been broken, autonomously aligned, self-healed after which pulled aside on a non-self-healing topic (to indicate the situation of the injury). (Picture: Bao Group, Stanford College)
|
A Novel Method
|
|
“We reported the primary multi-layer self-healing artificial digital pores and skin in 2012 in Nature Nanotechnology (“An electrically and mechanically self-healing composite with pressure- and flexion-sensitive properties for digital pores and skin functions”),” says Bao. “There was plenty of curiosity all over the world in pursuing multi-layer artificial pores and skin since then.” What units their present work aside is that the layers self-recognize and align with like layers throughout the therapeutic course of, restoring performance layer by layer as they heal. Present self-healing artificial skins have to be realigned manually—by people. Even a slight misalignment in layers would possibly compromise practical restoration.
|
|
The key is within the supplies. The spine of every layer is shaped of lengthy molecular chains linked periodically by dynamic hydrogen bonds, just like these holding the double-helix of DNA strands collectively, that enable the fabric to stretch repeatedly with out tearing. Rubber and latex are two well-known pure polymers, however there are numerous artificial polymers, too. The bottom line is to design polymer molecular constructions and select the correct mixture for every layer—first layer of 1 polymer, the second of one other and so forth.
|
|
The researchers used PPG (polypropylene glycol) and PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane, higher referred to as silicone). Each have rubber-like electrical and mechanical properties and biocompatibility and could be blended with nano- or microparticles to allow electrical conductivity. Critically, the chosen polymers and their respective composites are immiscible — they don’t combine with each other but, as a result of hydrogen bonding, they adhere to 1 one other effectively to create a sturdy, multilayer materials.
|
|
Each polymers have the benefit that when warmed they soften and circulation, however solidify as they cool. Thus, by warming the artificial pores and skin, the researchers had been in a position to pace the therapeutic course of. At room temperature, therapeutic can take so long as every week, however when heated to only 70 °C (158 F), the self-alignment and therapeutic occur in about 24 hours. The 2 supplies had been rigorously designed to have related viscous and elastic responses to exterior stress over an acceptable temperature vary.
|
|
“Pores and skin is sluggish to heal, too. I lower my finger the opposite day and it was nonetheless therapeutic 4 or 5 days later,” Cooper says. “For us, crucial half is that it heals to get better features with out our enter or effort.”
|
A Step Additional
|
|
With a profitable prototype, the researchers then took issues a step additional, working with Professor Renee Zhao at Stanford College, including magnetic supplies to their polymer layers, permitting the artificial pores and skin to not solely heal but in addition to self-assemble from separate items. “Combining with magnetic field-guided navigation and induction heating,” says Zhao, “we might be able to construct reconfigurable smooth robots that may change form and sense their deformation on demand.”
|
|
“Our long-term imaginative and prescient is to create gadgets that may get better from excessive injury. For instance, think about a tool that when torn into items and ripped aside, might reconstruct itself autonomously,” Cooper says, displaying a brief video of a number of items of stratified artificial pores and skin immersed in water. Drawn collectively magnetically, the items inch towards each other, ultimately reassembling. As they heal, their electrical conductivity returns, and an LED hooked up atop the fabric glows to show it.
|
|
Amongst their subsequent steps, the researchers will work to make the layers as skinny as attainable and towards creating layers of various operate. The present prototype was engineered to sense stress, and extra layers engineered to sense adjustments in temperature or pressure might be included.
|
|
When it comes to future imaginative and prescient, the crew imagines, probably, robots that might be swallowed in items after which self-assemble contained in the physique to carry out non-invasive medical remedies. Different functions embody multi-sensory, self-healing digital skins that form-fit to robots and supply them with a way of contact.
|

