Scientists at UMC Utrecht have made numerous improvements in volumetric bioprinting.
Bioprinting, the 3D printing of dwelling cells and tissues, is an additive manufacturing approach providing potential for medical functions. Nonetheless, 3D printing dwelling cells and tissue continues to pose numerous challenges.
The UMC Utrecht researchers have made three key developments on this subject: creating biologically purposeful areas in 3D printed cells; utilizing granular gels to optimize 3D bioprinted cells; and mixing volumetric bioprinting with soften electrowriting to 3D print blood vessels.
It’s hoped that these developments will assist to increase medical use of 3D bioprinting.
3D printing cells with biologically purposeful areas
One key innovation pertains to the organic performance of 3D printed cells.
Volumetric bioprinting, used at the side of specialised gels, permits cells to be 3D printed in a matter of seconds. Nonetheless, typical 3D bioprinting strategies don’t enable these cells to be precisely manipulated and positioned precisely the place they’re wanted. Furthermore, the gels can’t be edited to allow the event, progress and specialization of cells.
The researchers labored to allow chemical adjustments to the 3D printed supplies after the preliminary 3D bioprinting course of. To realize this, the researchers edited each the porosity of the gel, and the inner compounds which bind with different molecules within the gel.
“First we printed our gelatin-based constructs with the volumetric printer, then by infusing these constructs with biomolecules and photoinitiator, we may create complicated 3D motives contained in the gelatin buildings,” defined Marc Falandt, an creator of the Superior Supplies Applied sciences paper.
This makes it doable to volumetrically 3D bioprint tissue that may have progress components or bioactive proteins “painted” into them.
Falandt sees this as a significant step in creating sensible supplies that may be biochemically edited. “This method is extraordinarily promising for the creation of biofabricated scaffolds that might information cell conduct and improvement.”
Utilizing granular gels to 3D bioprint optimized cells
3D printed cells require particular consideration to make sure that they’ll survive and thrive. Furthermore, it’s critical that the cells can develop, transfer, and talk.
Extrusion 3D printing permits for a wide range of cell sorts to be deposited at excessive portions. Nonetheless, this course of is time-consuming, gravity dependent, and might trigger mechanical stress to the cells.
While volumetric bioprinting doesn’t possess the drawbacks in velocity or gravity dependence, it does distribute the cells randomly, and in low numbers. Furthermore, the cells can’t operate and talk successfully.
Subsequently, supplies resembling delicate hydrogels have to be used, as these enable for the self-organization and communication of cells. But, conventional delicate hydrogels pose issues on the subject of 3D print decision and form constancy.
The scientists employed granulated resins to beat these challenges.
“Granular gels are principally gel microparticles packed tightly collectively,” defined Davide Ribezzi, first creator of a examine posted to bioRxiv. “Packed microgel particles could be designed and customised to show a broad array of added helpful properties.”
Throughout extrusion 3D printing, cells and different chemical compounds could be shortly and precisely deposited within the resin. Volumetric 3D printing is then used to finish the method by creating the shapes across the extruded cells.
Experimentation with cells highlighted that granulated resins allow extra organic exercise after printing. Inside eight days of being 3D printed, stem cells had been capable of unfold out extra, epithelial cells created extra junctions, and neuron-like cells made extra connections.
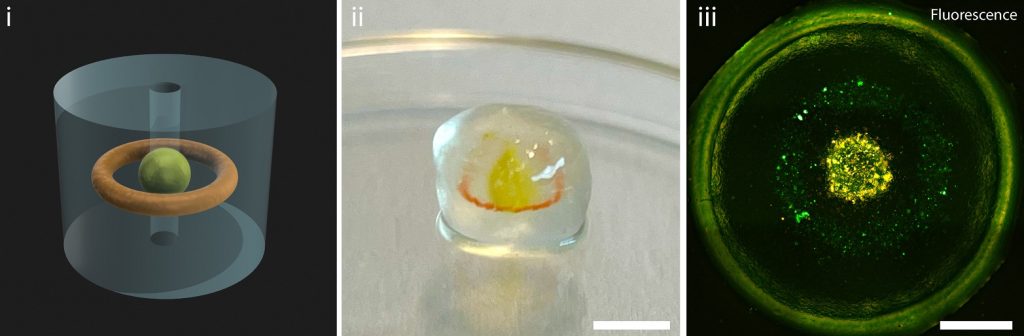
Merging bioprinting strategies for stronger, purposeful blood vessels
As a result of volumetric bioprinting makes use of cell-friendly gels, the ultimate 3D printed buildings are sometimes weak. This poses issues when producing blood vessels, which want to resist excessive stress and bending. Subsequently, the researchers mixed volumetric bioprinting with soften electrowriting to create stronger and extra sturdy buildings.
Soften electrowriting makes use of a slender filament of molten plastic to 3D print intricate and robust scaffolds. Nonetheless, because of the excessive temperatures concerned, electrowriting can’t immediately 3D print cells.
Thus, volumetric bioprinting was integrated to solidify cell-laden gels onto the scaffolds. The 3D printed tubular scaffold is submerged right into a vial of photoactive gel, after which positioned within the volumetric printer. The laser of the 3D printer can then selectively solidify the gel onto the scaffold.
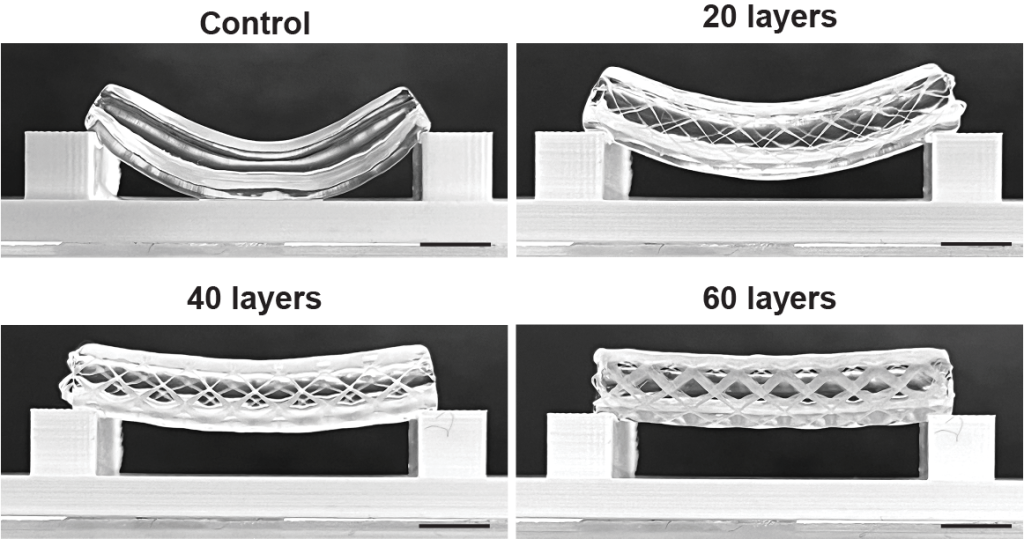
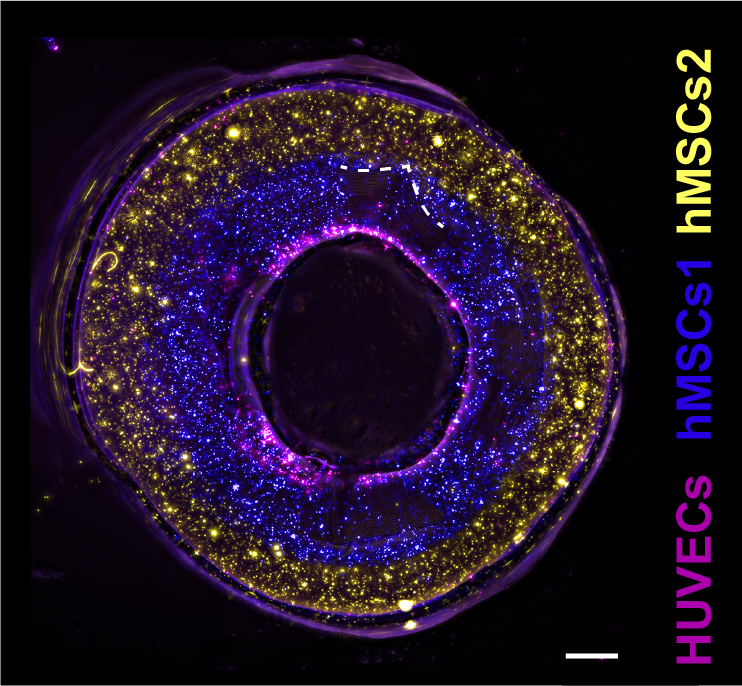
In a examine revealed within the Superior Supplies journal, researchers examined numerous scaffold thicknesses, and totally different placements of the bioprinted gels. The analysis group additionally 3D printed a proof of precept blood vessel with two layers of stem cells, and a layer of epithelial cells within the heart.
This design permits holes to be included within the facet of the 3D print, offering the chance for managed permeability of the vessel. Extra complicated buildings had been additionally produced, together with forked vessels, and vessels with venous valves.
“This was a proof of precept examine. What we now have to do is substitute the stem cells with purposeful cells which are a part of an actual blood vessel,” commented Gabriël Größbacher, lead creator of the examine.
Developments in 3D bioprinting
Earlier this yr 3D Programs introduced plans for a Regenerative Tissue Program (RPT) to develop and commercialize bioprinted human tissue. The primary RPT to be developed underneath the RPT is patient-specific regenerative breast tissue (RBT).
Utilizing 3D modeling and 3D bioprinting alongside a Digital Surgical Planning (VSP) system, 3D Programs can reportedly design and 3D print bio-integrative scaffolds that match the anatomy and physiology of the affected person.
Elsewhere, researchers on the College of Swansea are growing a 3D printed vegan nostril, for these requiring synthetic nostril transplants. On this course of, nanocellulose hydrogel and hyaluronic acid are used as bioink to 3D print a man-made cartilage scaffold. That is then cured by a organic catalyst to extend its power. The 3D printed scaffold is then bathed in an answer of the sufferers’ cartilage cells, earlier than being surgically implanted.
Subscribe to the 3D Printing Business publication to make sure you sustain with the newest 3D printing information. You may as well observe us on Twitter, like our Fb web page, and subscribe to the 3D Printing Business Youtube channel to entry extra unique content material.
Are you interested by working within the additive manufacturing trade? Go to 3D Printing Jobs to view a number of accessible roles and kickstart your profession.
Featured picture reveals the embedded printing of cells in a granular gel. Photograph through LevatoLab, UMC Utrecht.

