Researchers at Yale College, New Haven, have optimized a polymer-based mRNA automobile for focused lung supply and demonstrated the potential of the platform for mucosal vaccination in opposition to respiratory pathogens.
In a paper, “Polymer nanoparticles ship mRNA to the lung for mucosal vaccination,” printed in Science Translational Medication, the group introduces their creation of inhalable messenger RNA (mRNA) for therapeutic use.
Scientific analysis has been looking for an environment friendly and focused technique to ship mRNA to the lungs for varied therapeutic purposes, together with protein substitute therapies, gene enhancing and vaccination. The principle challenges have been sustaining mRNA stability and avoiding immune interference.
The Yale group created PACE (Polymerized Albumin Conjugates for mRNA Encapsulation) polymer formulations to ship native mRNA to the lungs. The researchers optimized PACE polyplexes to boost mRNA safety, transfection effectivity, and antigen presentation for efficient lung-specific therapeutic and vaccination methods.
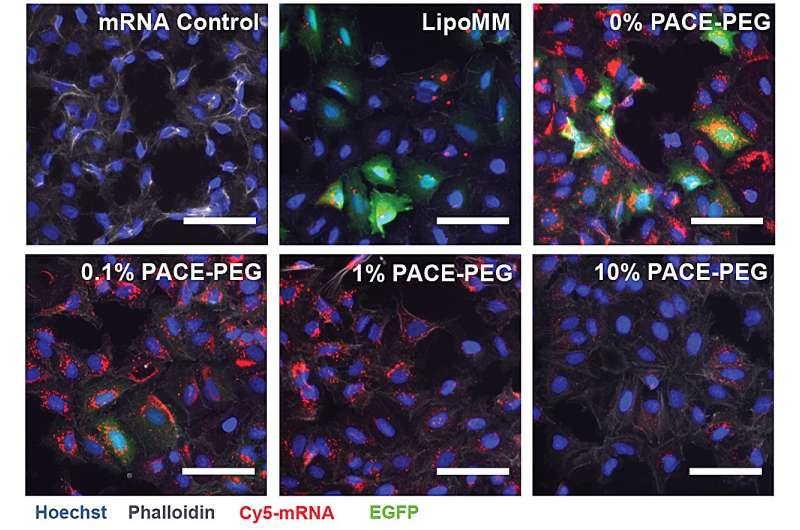
To stabilize PACE, an optimized ratio of polyethylene glycol (PEG) molecules have been built-in into the polymer construction throughout the enzymatic copolymerization course of, which stabilized the polyplexes and modified key traits. PEG was in a position to have an effect on the dimensions, floor cost, and different properties of the polyplexes, making them extra appropriate for loading and efficient at mRNA supply to lung cells.
The stabilized formulation carried out poorly in an in vitro cell tradition experiment. The researchers notice that conventional cell tradition strategies usually are not good predictors of supply programs, both positively or negatively. The setting inside the physique, particularly the lungs, interacts very in a different way than a group of cells. As an example, the mucosal surfaces are lacking, and people surfaces are precisely what the PACE-PEG system is designed to benefit from. The true take a look at would are available in vivo with a mouse mannequin.
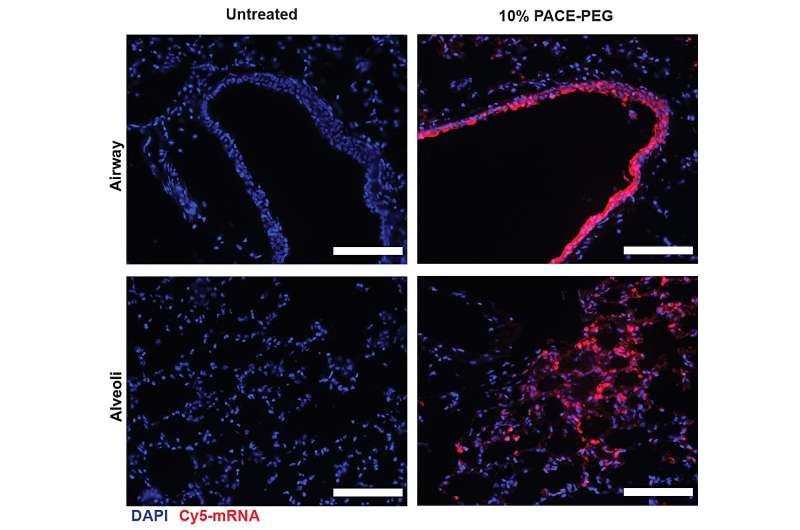
The researchers encapsulated mRNA encoding the spike protein from SARS-CoV-2 into PACE and inoculated mice inclined to SARS-CoV-2 an infection. Mice obtained a 10-μg dose of PACE-mRNA delivered intranasally on days 0 and 28. The event of adaptive immunity within the mediastinal lymph nodes was examined and confirmed 14 days after the increase.
After assessing the native immune response, the researchers examined lung tissues, blood serum, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for native and systemic antigen-specific T-cell and antibody responses. Transfection occurred primarily in lung epithelial cells and antigen-presenting cells, two cell sorts which are related targets for pulmonary ailments
The vaccination efficiently elevated spike protein-specific CD8+ T cells within the lung tissue and circulating CD8+ T cells within the bloodstream. CD8+ T cells expressed markers indicative of tissue-resident reminiscence. Each circulating and mucosal IgG antibodies have been discovered at considerably greater concentrations in vaccinated mice.
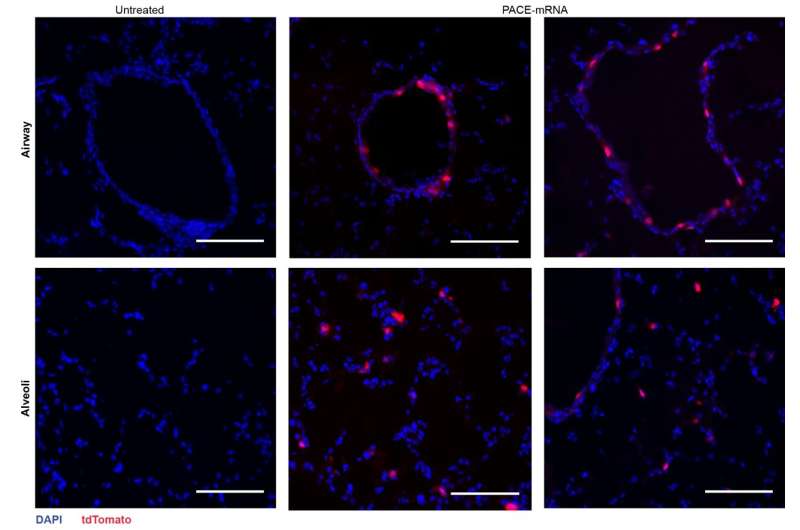
Mice have been then launched to a deadly dose of SARS-CoV-2. PACE-mRNA vaccination considerably lowered the viral burden within the lungs and improved the load and survival of the vaccinated mice. This safety was attributed to the spike protein-specific immune response induced by the vaccination.
The management group confirmed no proof of a spike protein-specific immune response and didn’t exhibit lowered viral load or improved survival after the viral problem.
The examine presents PACE-mRNA polyplexes as a promising technique for environment friendly and focused mRNA supply to the lungs with potential advantages for each therapeutic protein expression and mucosal vaccination in opposition to respiratory pathogens.
The examine additionally illustrates the significance of animal fashions versus cell tradition alone in figuring out real-world results. The constructive outcomes point out that extra analysis is warranted, with additional testing deliberate on bigger animal fashions.
Extra info:
Alexandra Suberi et al, Polymer nanoparticles ship mRNA to the lung for mucosal vaccination, Science Translational Medication (2023). DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abq0603
© 2023 Science X Community
Quotation:
Sniffing nanoparticles loaded with mRNA might result in superior lung therapeutics (2023, August 18)
retrieved 20 August 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-08-sniffing-nanoparticles-mrna-advanced-lung.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.

